Introduction
Understanding how the body maintains stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health. Hormones play a vital role in this process, ensuring that blood sugar levels remain within a narrow range. When blood sugar levels drop below the normal range, the body initiates a series of responses to raise them back to optimal levels.
Insulin: The Key Regulator
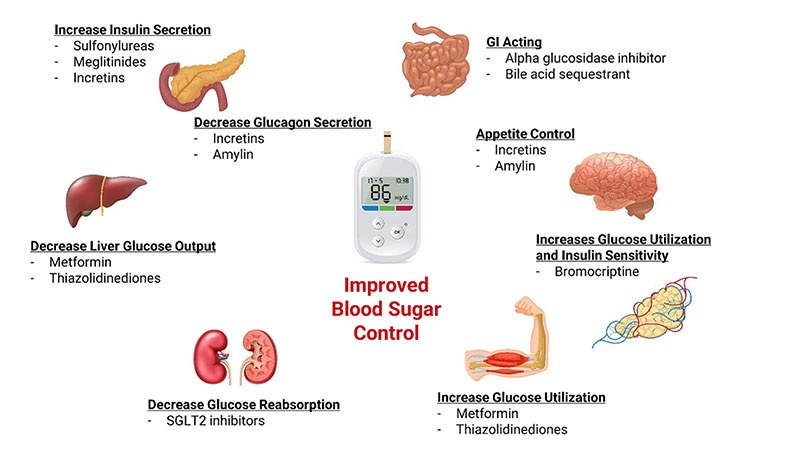
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for future use. When blood sugar levels rise, such as after a meal, the pancreas releases insulin to lower them by promoting glucose uptake by cells.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Glucagon: The Counterbalance
While insulin lowers blood sugar levels, another hormone called glucagon works in opposition to raise them when they fall too low. Glucagon is also produced by the pancreas but serves the opposite function of insulin. When blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas releases glucagon to stimulate the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels.
Hormonal Response to Low Blood Sugar
When blood sugar levels decrease, the body initiates a hormonal response to prevent hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by dangerously low blood sugar levels. This response involves the rapid secretion of glucagon and other hormones to counteract the drop in blood sugar.
Release of Glucagon
The pancreas detects the decrease in blood sugar levels and responds by releasing glucagon into the bloodstream. Glucagon then signals the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream to raise blood sugar levels.
Glucagon's Action
Once released, glucagon promotes the breakdown of glycogen into glucose through a process called glycogenolysis. Additionally, it stimulates gluconeogenesis, the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids and glycerol. These actions help raise blood sugar levels to maintain adequate energy supply to cells.
Other Hormones Involved
In addition to insulin and glucagon, other hormones such as cortisol, epinephrine (adrenaline), and growth hormone also play a role in regulating blood sugar levels. These hormones can either increase blood sugar levels (such as cortisol and epinephrine) or promote glucose uptake by cells (such as insulin and growth hormone), depending on the body's needs.
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
When blood sugar levels drop too low, individuals may experience symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, sweating, confusion, and hunger. These symptoms serve as warning signs that prompt the individual to consume glucose-containing foods or beverages to raise their blood sugar levels quickly.
Consequences of Untreated Hypoglycemia
Untreated hypoglycemia can lead to more severe symptoms, including seizures, loss of consciousness, and, in extreme cases, coma or death. Therefore, it is essential to recognize and promptly treat low blood sugar levels to prevent complications.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Factors Influencing Hormonal Response
Several factors can influence the body's hormonal response to low blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, medications (such as insulin or diabetes medications), stress, and underlying health conditions (such as diabetes or hormonal disorders).
Management of Hypoglycemia
Managing hypoglycemia involves both preventive measures and treatment strategies. Preventive measures include maintaining a balanced diet, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. Treatment strategies for low blood sugar episodes may include consuming fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, to raise blood sugar levels quickly.
Preventive Measures
To maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemia, individuals should focus on adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including eating regular meals and snacks, monitoring carbohydrate intake, staying hydrated, getting an adequate amount of sleep, and managing stress effectively.
Impact of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in conditions like diabetes or hormonal disorders, can disrupt the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Uncontrolled diabetes, for example, can lead to chronically high or low blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you experience frequent or severe episodes of low blood sugar, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management. Your healthcare provider can help identify the underlying cause of your low blood sugar levels and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your needs effectively.
Conclusion
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Hormones such as insulin and glucagon play a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels and preventing hypoglycemia. By understanding how these hormones function and taking proactive steps to support their balance, individuals can minimize the risk of low blood sugar episodes and associated complications.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
What causes low blood sugar levels?
-
How can I raise my blood sugar quickly?
-
Is low blood sugar dangerous?

No comments yet