Introduction to Blood Sugar Regulation
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. Our bodies have finely tuned mechanisms to regulate blood sugar levels, ensuring they remain within a narrow range to support vital functions.
Understanding Hypoglycemia
Definition of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia refers to a condition where blood sugar levels drop below normal levels. This can occur for various reasons, including excessive insulin production, certain medications, or prolonged fasting.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Symptoms of hypoglycemia can vary from mild to severe and may include sweating, shakiness, confusion, dizziness, and in extreme cases, loss of consciousness.
Role of Hormones in Blood Sugar Regulation
Hormones play a key role in regulating blood sugar levels, ensuring they are maintained within a healthy range.
Insulin: The Blood Sugar Regulator
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. It promotes the storage of glucose in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen, lowering blood sugar levels.
Glucagon: Counteracting Low Blood Sugar
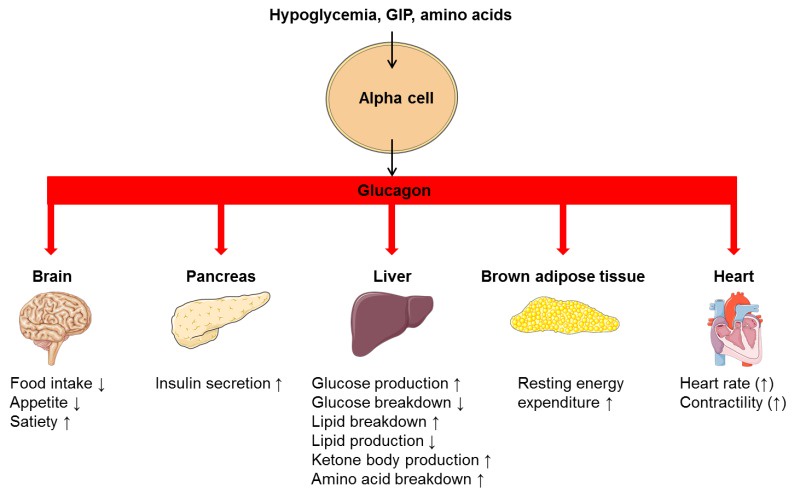
Glucagon is another hormone produced by the pancreas, but it has the opposite effect of insulin. When blood sugar levels drop too low, glucagon is released to stimulate the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels.
Hormonal Response to Low Blood Sugar
Overview of Hormones Involved
In addition to insulin and glucagon, other hormones also play a role in regulating blood sugar levels, including adrenaline and cortisol.
Focus on Glucagon
Glucagon plays a crucial role in counteracting low blood sugar levels, ensuring that cells have an adequate supply of glucose for energy.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Glucagon: The Hormone Counteracting Low Blood Sugar
Function of Glucagon
Glucagon acts on the liver to stimulate the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the bloodstream to raise blood sugar levels.
How Glucagon Raises Blood Sugar Levels
By promoting the conversion of glycogen into glucose and stimulating glucose production by the liver, glucagon effectively raises blood sugar levels in response to low levels.
Regulation Mechanism of Glucagon
Triggers for Glucagon Release
Several factors can trigger the release of glucagon, including low blood sugar levels, stress, and certain hormones like adrenaline.
Role of the Pancreas
The pancreas plays a central role in regulating the release of glucagon in response to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Other Hormonal Responses to Low Blood Sugar
Adrenaline's Role in Hypoglycemia
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is released in response to stress or low blood sugar levels, helping to raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose from the liver.
Cortisol's Influence on Blood Sugar Levels
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, can also affect blood sugar levels by promoting glucose production in the liver.
Impacts of Hormonal Response to Low Blood Sugar
Short-Term Effects
In the short term, hormonal responses to low blood sugar help prevent hypoglycemia and ensure cells have a constant supply of glucose for energy.
Long-Term Effects
However, chronic fluctuations in blood sugar levels and dysregulation of hormones can lead to long-term health complications, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Factors Affecting Hormonal Response
Individual Variations
The hormonal response to low blood sugar can vary from person to person, depending on factors such as genetics, age, and overall health.
External Factors
External factors such as diet, exercise, and stress can also influence the hormonal response to low blood sugar levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Diagnosing Low Blood Sugar
Diagnosing hypoglycemia typically involves measuring blood sugar levels and assessing symptoms.
Management Strategies
Treatment for hypoglycemia often involves consuming fast-acting carbohydrates to raise blood sugar levels quickly, followed by a snack or meal to prevent further drops.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Preventing Hypoglycemia
Dietary Considerations
Maintaining a balanced diet with regular meals and snacks can help prevent episodes of hypoglycemia.
Medication Adjustments
For individuals with diabetes or other conditions that increase the risk of hypoglycemia, adjusting medication doses and timing may be necessary to prevent low blood sugar levels.

No comments yet