The human body operates like a finely tuned machine, with various hormones playing crucial roles in maintaining balance and harmony. One such hormone, cortisol, produced in the adrenal cortex, holds significance in regulating blood sugar levels. In this article, we'll delve into the intricate mechanisms of cortisol and its impact on blood sugar regulation, along with strategies for maintaining optimal cortisol levels naturally.
Introduction to Cortisol
Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," serves multiple functions in the body. Primarily produced in the adrenal glands, cortisol plays a key role in metabolism, immune response, and stress management.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
The Adrenal Cortex: Home of Cortisol Production
Situated atop the kidneys, the adrenal glands consist of two main parts: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. Cortisol is synthesized in the outer layer, known as the adrenal cortex, through a complex biochemical process involving cholesterol and various enzymes.
Regulation of Blood Sugar Levels
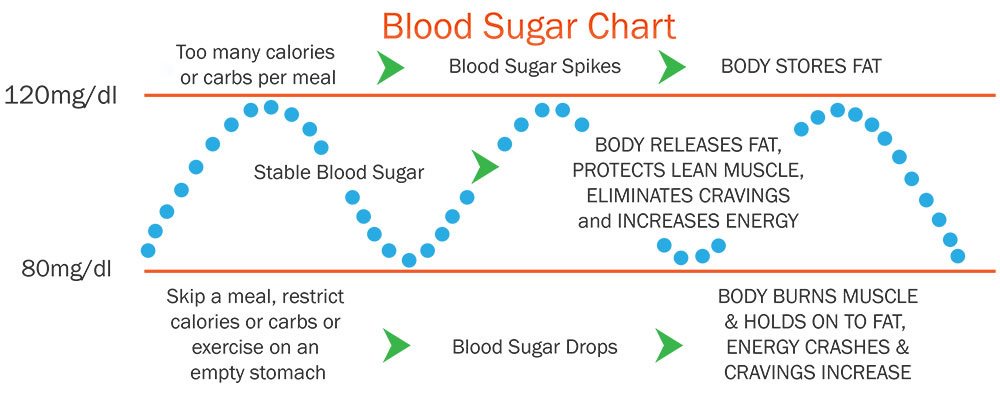
Blood sugar, or glucose, serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and wellbeing. Hormones such as insulin and glucagon play pivotal roles in regulating glucose levels within a narrow range.
Cortisol and Blood Sugar Regulation
While insulin and glucagon are well-known for their roles in blood sugar regulation, cortisol also exerts significant influence in this process. During times of stress or fasting, cortisol stimulates gluconeogenesis, the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and glycerol.
Stress Response and Cortisol Release
The body's response to stress, often referred to as the "fight or flight" response, triggers the release of cortisol as part of a complex physiological reaction. Cortisol mobilizes energy stores, increases heart rate, and suppresses non-essential functions such as digestion and reproductive processes.
Impact of Cortisol Imbalance
While cortisol is essential for survival, both excess and insufficient levels can lead to adverse health effects. Conditions such as Cushing's syndrome, characterized by hypercortisolism, can result in weight gain, hypertension, and impaired immune function. On the other hand, hypocortisolism, as seen in Addison's disease, may manifest as fatigue, weight loss, and hypoglycemia.
Health Implications of Cortisol Dysregulation
The dysregulation of cortisol levels has far-reaching implications for health and wellbeing. Chronic stress, characterized by prolonged elevation of cortisol, has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Factors Affecting Cortisol Levels
Various factors can influence cortisol production and secretion. Chronic stress, inadequate sleep, poor dietary choices, and certain medical conditions can disrupt the body's cortisol balance, leading to adverse health outcomes.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Managing Cortisol Levels Naturally
Fortunately, several strategies can help maintain optimal cortisol levels naturally. Stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help mitigate the harmful effects of chronic stress on cortisol regulation.
Medical Interventions for Cortisol Imbalance
In cases where cortisol levels are significantly dysregulated, medical interventions may be necessary. Pharmacological treatments such as cortisol receptor antagonists or inhibitors of cortisol synthesis may be prescribed to normalize cortisol levels and alleviate symptoms associated with cortisol imbalance.
Cortisol and Chronic Conditions
Cortisol dysregulation is often observed in individuals with chronic diseases such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and mood disorders. Managing cortisol levels alongside the underlying condition is essential for optimizing health outcomes and improving quality of life.
Cortisol and Weight Management
The relationship between cortisol and weight management is complex. While cortisol promotes the breakdown of fat stores for energy during times of stress, chronic elevation of cortisol levels can lead to abdominal obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and prioritizing stress management are key components of a comprehensive weight management strategy.
Cortisol and Exercise
Exercise can modulate cortisol levels, with both acute and chronic effects depending on factors such as exercise intensity, duration, and individual fitness levels. Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise has been shown to reduce cortisol levels and alleviate symptoms of stress, whereas high-intensity or prolonged exercise may temporarily elevate cortisol levels.
Click & Get Sugar Defender Here>>>>>>>
Diet and Cortisol
Nutritional factors play a significant role in cortisol regulation. Consuming a diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can support adrenal health and promote balanced cortisol levels. Additionally, avoiding excessive caffeine, sugar, and processed foods can help prevent spikes in cortisol levels.

No comments yet