Direct Attached Storage (DAS) stands out as a vigorous and solid choice for companies looking for proximity, performance, and seamless data accessibility.
As organizations wrestle with rising data volumes, the requirement for Direct Attached storage solutions that offer high-speed access, low latency, and clear management becomes increasingly basic.
This article dives into the complexities of Direct Attached Storage, investigating its advantages, use cases, and how it tends to meet the squeezing demands of modern data-driven undertakings.
Understanding Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
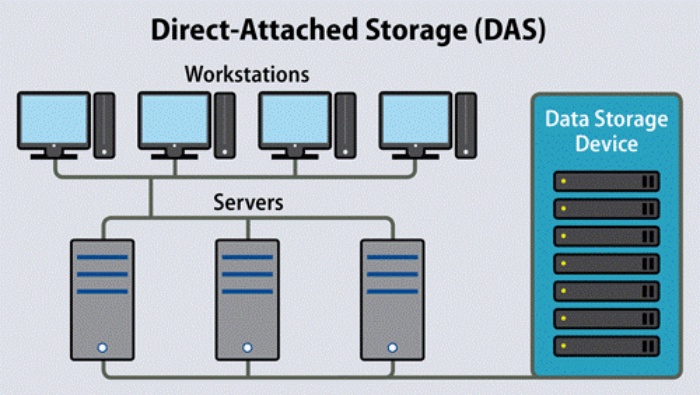
Direct Attached Storage, as the name suggests, includes directly interfacing storage devices to a solitary server or a group of servers without the requirement for a network.
Unlike Network Attached Storage (NAS) or Storage Area Network (SAN), which depend on a network to empower different users to get to the storage assets, DAS is a more localized approach.
This proximity-driven plan has critical ramifications for performance and data accessibility.
Types of Direct Attached Storage
-
Internal DAS
- Storage devices, such as hard drives or SSDs, are directly connected to the server's internal storage regulator.
- Typically used in smaller arrangements or individual systems where scalability is not critical.
-
External DAS
- Uses storage devices housed in external fenced-in areas that are associated with the server through interfaces like USB, eSATA, or Thunderbolt.
- Gives adaptability and scalability, making it reasonable for conditions where an extra storage limit is a regular prerequisite.
Proximity of DAS Server: The Advantage of Localized Storage
One of the vital qualities of DAS is its proximity to the host server. In situations where quick data access is vital, limiting the actual distance between the storage and handling parts can significantly affect performance.
-
Low Latency
- In DAS arrangements, data ventures brief distances inside the limits of a solitary server or a firmly associated group. This outcome is negligible latency, adding to quicker data recovery and storage activities.
- Applications that request ongoing data handling, for example, financial exchanges or video altering, benefit fundamentally from the low-latency nature of DAS.
-
High Bandwidth
- The direct association between the storage devices and the server allows for higher bandwidth compared with network-subordinate storage solutions.
- This expanded bandwidth means quicker data movement rates, making DAS appropriate for workloads that include enormous document measures or require fast access to huge datasets.
Performance of DAS Server: Meeting the Demands of Modern Workloads
In a time where data-concentrated workloads are the norm as opposed to the exemption, performance is a basic consideration for any storage solution. DAS succeeds in providing the speed and responsiveness expected by a different scope of uses and businesses.
-
Optimized for Specific Workloads
- DAS designs may be modified to meet the specific performance necessities of various workloads. This customization allows associations to upgrade storage assets given their novel necessities.
- For instance, high-performance computing (HPC) applications, scientific simulations, and database systems frequently request low-latency and high-throughput storage solutions, which DAS can promptly provide.
-
Scalability without Sacrificing Performance
- External DAS solutions, furnished with numerous drive coves and backing for different strike arrangements, offer scalability without compromising performance.
- As storage needs develop, associations can extend their DAS arrangements by adding more drives or moving up to higher-limit storage devices while keeping up with the advantages of localized storage.
-
Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
- Numerous DAS arrangements support assault setups, upgrading data unwavering quality by executing redundancy and fault tolerance instruments.
- Redundant Array of Independent Disks (Strike) levels, like Attack 1 or Assault 10, can be utilized to guarantee data honesty and accessibility even in case of drive disappointments.
Data Accessibility: Seamless and Direct
Productive data accessibility is the foundation of any storage solution's viability. DAS, with its direct association with the host server, succeeds in providing a clear and solid method for getting data.
-
No Network Bottlenecks
- Unlike network-based storage solutions, where data access is dependent upon likely bottlenecks and conflict, DAS works independently of the network.
- This freedom guarantees steady and unsurprising data access times, making DAS appropriate for applications where each millisecond matters.
-
Isolation and Security
- DAS designs intrinsically give a degree of isolation, as the storage is directly associated with the host server and isn't imparted to different systems.
- This isolation upgrades security, diminishing the assault surface compared with networked storage solutions. Unapproved access endeavors are restricted to the actual proximity of the DAS arrangement.
-
Simplified Management
- Overseeing DAS is frequently less complex than networked storage solutions. There are no perplexing network arrangements or conventions to explore.
- This effortlessness prompts quicker arrangement times, decreased upkeep above, and simplicity of investigation, adding to an additional smoothed-out data management process.
Use Cases: Where DAS Shines
Direct Attached Storage finds application in different situations, each utilizing its assets to address specific prerequisites.
-
Media and Entertainment
- Video editing, delivering, and content creation benefit from the high-speed and low-latency access that DAS gives.
- Enormous media documents can be gotten to and controlled progressively, upgrading the proficiency of creation workflows.
-
Financial Services
- High-recurrence exchange stages depend on quick data access to execute exchanges with negligible latency. DAS guarantees that market data is rapidly and dependably accessible to exchanging systems.
- Financial investigation and display likewise benefit from the performance advantages of DAS.
-
Scientific Research and Simulation
- Scientific simulations, research projects, and computational displays frequently include huge datasets and request high-performance storage.
- DAS setups can be custom-fitted to meet the specific I/O prerequisites of scientific applications, resulting in quicker data handling.
-
Database Systems
- Database servers, where fast admittance to put away data is significant, can profit from the low-latency qualities of DAS.
- Conditional databases, data warehouses, and other database-escalated applications can achieve ideal performance with a very well-planned DAS arrangement.
-
Backup and Archiving
- DAS is a solid decision for backup and archiving purposes, particularly in situations where the emphasis is on speedy data recovery.
- The direct association between the storage and the backup server guarantees that backup and recuperation activities are quick and productive.
Conclusion
Direct Attached Storage (DAS) remains sturdy in the domain of data storage, offering proximity, performance, and clear data accessibility. Its direct association with the host server limits latency, guarantees high-speed data access, and works on management. As associations wrestle with raising data volumes and various workloads, DAS ends up being a flexible solution, finding applications in ventures going from media and entertainment to financial services and scientific research.
Read More: HOW SAP HANA SIMPLIFIES IT LANDSCAPES AND BOOSTS OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY

No comments yet