In the realm of manufacturing, plastic injection molding stands out as a cornerstone process for producing parts in large volumes. This method, widely employed for its efficiency, involves injecting molten materials into meticulously crafted molds. The key materials include metals, glasses, elastomers, and thermoplastics, with the last being the most prevalent in this manufacturing technique.
Unveiling the Process
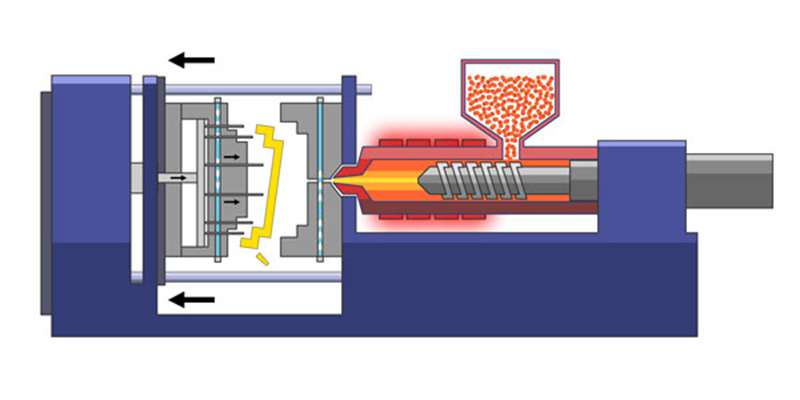
The injection molding process commences with the creation of a precision-machined mold, typically crafted from metals such as aluminum or steel. The mold plays a pivotal role in shaping the final product. Once the mold is ready, the material for the part is introduced into a heated barrel, where a helical-shaped screw mixes it thoroughly. Subsequently, the molten material is injected into the mold cavity, solidifying into the desired shape as it cools.
To expedite the cooling phase, cooling lines circulate water or oil from an external temperature controller. The mold tools, mounted on platens, open post-solidification, facilitating the ejection of the part through ejector pins.
Enhancing Possibilities: Two-Shot Molding
Diversifying the capabilities of injection molding, two-shot molding allows the combination of different materials in a single part. This technique opens avenues for adding a soft touch, introducing vibrant colors, or imbuing varied performance characteristics in the final product.
Navigating Mould Considerations
When embarking on injection molding, several crucial considerations come to the fore:
-
Financial Prudence: Initial costs can be substantial, encompassing machinery and mold creation.
-
Production Quantity: Evaluating the volume of parts required is pivotal to ascertain the cost-effectiveness of injection molding.
-
Design Optimization: Simplifying part geometry and minimizing components streamline the injection molding process.
-
Production Efficiency: Minimizing cycle time, utilizing hot runner molds, and strategic tooling contribute to cost savings and efficient production.
Cost-Effective Strategies
While injection molding can be an expensive endeavor, adopting certain strategies can mitigate costs:
-
Undercut Elimination: Designing parts without undercuts reduces complexity and cost.
-
Feature Streamlining: Removing unnecessary features minimizes production intricacies.
-
Core Cavity Approach: Utilizing a core cavity design optimizes mold complexity and reduces costs.
Exploring Applications
Injection molding finds extensive application in crafting various products, ranging from everyday items like bottle tops to complex components like car body panels. Its prevalence lies in scenarios demanding the mass production of identical parts.
Plastic Molds and Materials
Diving deeper into the realm of plastic injection molding, the materials and molds employed are critical considerations. The choice of plastics, including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), and Polycarbonate (PC), influences the properties of the final product.
Environmental Impact and Cost Dynamics
Addressing environmental concerns, modern injection molding machinery showcases enhanced efficiency, using 20-50% less energy than a decade ago. The process minimizes material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
On the cost front, the correlation between mold costs and the number of cavities is crucial. Rubber injection molding emerges as the most cost-effective, yielding durable products with efficient vulcanization processes.
Deciphering the Cost Code
Calculating injection molding costs involves factoring in material costs, design, process and profit, VAT, try-out costs, and packing and shipping costs. While mold tools incur a significant upfront cost, actual production costs remain relatively low.
The Plastic Landscape in Injection Molding
With over 85,000 plastic material options, the injection molding arena presents a diverse landscape. The prominent thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers, including HDPE and LDPE, ABS, PC, and more, offer a spectrum of properties suitable for various applications.
Conclusion: Mastering Injection Molding Dynamics
In conclusion, injection molding reigns supreme in high-volume part production. While the initial investment in tooling may seem formidable, the long-term benefits of cost-effective production, minimal wastage, and the ability to create near-identical parts position injection molding as a pivotal player in modern manufacturing. Mastering the dynamics of plastic molds, materials, and cost considerations ensures optimal outcomes in the realm of injection molding.

No comments yet