Introduction:
Homeownership represents a significant milestone in one's life, symbolizing stability, security, and a place to call one's own. However, amidst the joy of owning a home, there are essential considerations that should not be overlooked, one of which is indoor air quality. Radon, a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas, poses a serious health risk when present in elevated concentrations indoors. Despite its potential dangers, radon often goes undetected, leading to long-term health implications for occupants. In this comprehensive article, we explore the importance of radon inspection for homeowners, shedding light on its health implications, testing methods, regulatory considerations, and proactive measures to mitigate radon risks.
Understanding Radon and its Health Implications:
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas formed by the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It enters buildings through cracks in foundations, gaps in walls, floors, and other openings, accumulating to potentially hazardous levels indoors. Prolonged exposure to elevated radon levels increases the risk of lung cancer, making radon the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), radon exposure is responsible for approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths annually in the United States alone. Given these risks, radon inspection is essential for identifying and mitigating radon hazards in residential environments.
The Importance of Radon Inspection for Homeowners:
Radon inspection plays a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of homeowners and their families. Here's why every homeowner should consider radon inspection:
Health Protection:
The primary reason for radon inspection is to protect the health of occupants. Elevated radon levels pose a significant risk of lung cancer, particularly for individuals who spend extended periods indoors, such as homeowners, tenants, and their families. By conducting radon inspections, homeowners can identify potential radon hazards and take proactive measures to mitigate radon risks, thereby reducing the likelihood of adverse health effects.
Early Detection:
Radon inspection allows homeowners to detect radon hazards early before they escalate into more significant problems. Unlike other household hazards that may exhibit visible signs or symptoms, radon is invisible and odorless, making it difficult to detect without proper testing. By conducting radon inspections, homeowners can identify radon sources, assess radon levels, and implement timely mitigation measures to address radon hazards effectively.
Property Value Preservation:
Radon inspection can help preserve the value of residential properties by addressing potential radon hazards and ensuring a safe living environment. Properties with documented radon testing and mitigation measures in place may command higher resale values and attract discerning buyers concerned about indoor air quality. Additionally, addressing radon hazards proactively can help homeowners avoid costly repairs, liability issues, and potential legal disputes in the future.
Radon Testing Methods for Homeowners:
Several radon testing methods are available for evaluating indoor radon levels in residential properties. The two primary testing methods suitable for homeowners are short-term and long-term radon tests:
Short-term Radon Tests:
Short-term radon tests provide a snapshot of radon levels over a brief period, typically two to seven days. These tests utilize passive devices such as charcoal canisters, alpha track detectors, or electret ion chambers to absorb or detect radon gas. Short-term tests offer a quick and cost-effective assessment of radon levels but may not capture long-term fluctuations or seasonal variations.
Long-term Radon Tests:
Long-term radon tests monitor radon levels over an extended period, usually three months to one year. These tests provide a more comprehensive assessment of average radon concentrations in a property, accounting for seasonal variations and fluctuations. Long-term tests are recommended for obtaining reliable and representative radon data for decision-making purposes.
Selecting the appropriate radon testing method depends on various factors, including the homeowner's preferences, property characteristics, and testing objectives. Both short-term and long-term tests can provide valuable insights into indoor radon levels and help homeowners make informed decisions about radon mitigation measures.
Regulatory Considerations for Radon Inspection:
In the United States, radon testing and mitigation activities are subject to various federal, state, and local regulations. While federal regulations do not mandate radon testing in residential properties, many states and local jurisdictions have enacted laws and regulations requiring radon testing as part of real estate transactions. Key regulatory considerations for radon inspection include:
Disclosure Requirements:
Real estate professionals and home sellers may be required to disclose known radon hazards and provide radon testing reports to prospective buyers as part of property disclosures. Failure to disclose radon hazards or provide accurate testing information can result in legal liabilities and financial consequences for sellers.
Real Estate Transactions:
Radon inspection may be included as a contingency in real estate purchase contracts, allowing buyers to conduct radon tests during the inspection period. Buyers may negotiate with sellers to address radon mitigation measures or request concessions based on test results. Real estate agents play a vital role in facilitating radon inspection and ensuring compliance with contractual obligations.
Radon Mitigation Requirements:
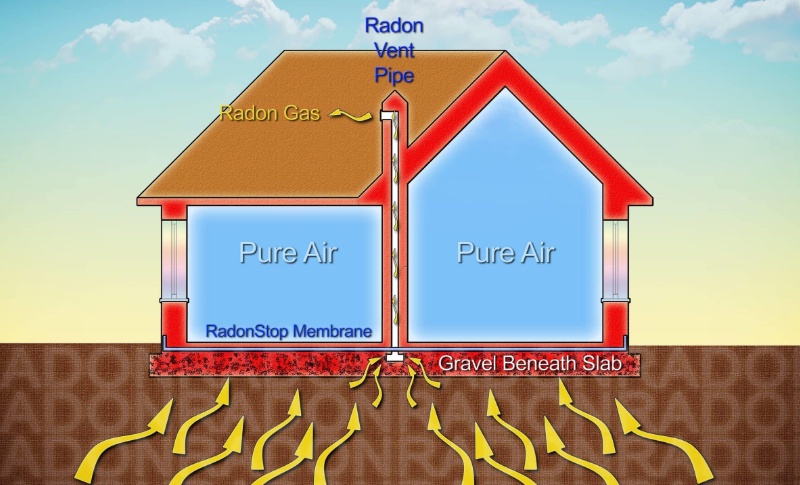
If radon testing reveals elevated radon levels in a property, homeowners may be required to implement radon mitigation measures to reduce radon concentrations to acceptable levels. Radon mitigation typically involves installing radon mitigation systems, such as sub-slab depressurization or ventilation systems, to mitigate radon risks effectively. Homeowners should ensure that radon mitigation measures comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Best Practices for Homeowners:
To ensure effective radon inspection and mitigation, homeowners should follow these best practices:
Schedule Regular Radon Testing:
Schedule regular radon testing to monitor indoor radon levels and identify potential radon hazards. Consider conducting both short-term and long-term radon tests to obtain comprehensive radon data and assess radon risks accurately.
Address Radon Hazards Promptly:
If radon testing reveals elevated radon levels in a property, take prompt action to address radon hazards and implement mitigation measures. Work with qualified radon mitigation professionals to design and install appropriate radon mitigation systems tailored to your property's needs.
Educate Yourself About Radon:
Familiarize yourself with the health risks associated with radon exposure, common radon testing methods, and radon mitigation techniques. Stay informed about radon regulations and guidelines in your area and seek guidance from reputable sources, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or state radon programs.
Maintain Radon Mitigation Systems:
Regularly maintain radon mitigation systems to ensure their continued effectiveness in reducing radon concentrations. Perform routine inspections, monitor system performance, and address any issues or malfunctions promptly to prevent radon hazards from reemerging.
Conclusion:
Radon inspection is a critical component of homeownership, essential for safeguarding health, ensuring safety, and preserving property value. By conducting radon inspections, homeowners can identify potential radon hazards, assess radon levels, and implement effective mitigation measures to mitigate radon risks. Regulatory compliance, proactive testing, and timely mitigation efforts contribute to creating safe and healthy homes that promote well-being and quality of life for occupants. Remember, when it comes to radon inspection, prioritizing health and safety is paramount for homeowners and their families.

No comments yet