Periodontology, the branch of dentistry dedicated to the study and treatment of the supporting structures of the teeth, plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health and overall well-being. Within the United Kingdom, periodontal diseases pose significant challenges, affecting a considerable portion of the population. This article delves into the landscape of periodontology and periodontal diseases in the UK, exploring their prevalence, impact, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding Periodontal Diseases:
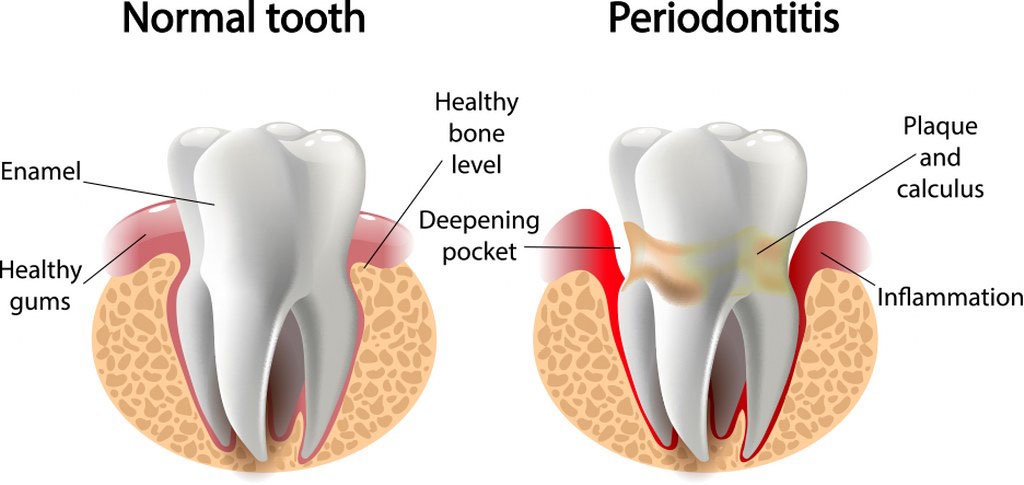
Periodontal diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. Gingivitis, the mildest form of periodontal disease, involves inflammation of the gingival tissues, often accompanied by bleeding and swelling. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition characterized by the destruction of the supporting bone and eventual tooth loss.
Prevalence in the UK:
Periodontal diseases are widespread in the UK, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. According to the Adult Dental Health Survey conducted by Public Health England, approximately 45% of adults in England have moderate to severe periodontitis, with prevalence rates varying across different age groups and socioeconomic strata. Additionally, research suggests a higher prevalence of periodontal diseases among certain populations, such as smokers, diabetics, and individuals with poor oral hygiene habits.
Impact on Oral Health and General Well-being:
The consequences of untreated periodontal diseases extend beyond oral health, impacting overall well-being and quality of life. Periodontitis has been linked to various systemic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Moreover, the psychological effects of periodontal diseases, such as embarrassment due to tooth loss or halitosis, can significantly affect an individual's self-esteem and social interactions.
Treatment Modalities:
The management of periodontal diseases typically involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical interventions aimed at controlling infection, reducing inflammation, and restoring periodontal health. Non-surgical treatments, such as scaling and root planing (commonly known as deep cleaning), aim to remove plaque and calculus from the tooth surfaces and root surfaces below the gumline. Adjunctive therapies, including locally administered antimicrobials and host modulation agents, may be employed to enhance treatment outcomes.
In cases of advanced periodontitis where significant tissue destruction has occurred, surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration may be necessary to regenerate lost tissues and improve periodontal support around the teeth. Furthermore, advances in regenerative techniques and tissue engineering hold promise for enhancing the predictability and long-term success of periodontal treatments.
Preventive Strategies:
Prevention lies at the core of effective periodontal care, emphasizing the importance of regular dental visits, thorough oral hygiene practices, and lifestyle modifications. Dental professionals play a pivotal role in educating patients about the risk factors associated with periodontal diseases and empowering them to adopt healthy behaviors that promote optimal oral health.
Key preventive strategies include:
Routine Dental Check-ups: Regular dental examinations enable early detection and intervention for periodontal diseases, allowing for timely management and prevention of disease progression.
Effective Oral Hygiene: Proper brushing, flossing, and interdental cleaning techniques are essential for removing plaque and preventing the buildup of calculus, reducing the risk of gingival inflammation and periodontal disease.
Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal diseases, impairing the body's ability to combat infection and compromising periodontal health. Smoking cessation interventions can significantly reduce the risk of periodontal disease progression.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a balanced diet, managing stress, and maintaining overall health contribute to optimal periodontal health and support the body's natural defenses against periodontal diseases.
Advancements in Periodontal Research and Practice:
The field of periodontology continues to evolve, driven by ongoing research efforts aimed at understanding the underlying mechanisms of periodontal diseases and developing innovative treatment modalities. Emerging trends in periodontal research include the role of host-microbiome interactions, the impact of genetic factors on periodontal susceptibility, and the development of personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient needs.
Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as digital imaging, laser therapy, and minimally invasive surgical techniques, have transformed the delivery of periodontal care, enabling more precise diagnosis and treatment with reduced patient discomfort and downtime. These innovations contribute to improved treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction within the realm of periodontology.
Conclusion:
Periodontology and periodontal diseases represent critical components of oral health care within the United Kingdom. With a significant prevalence of periodontal diseases across the population, there is a pressing need for comprehensive preventive measures, early detection, and effective treatment interventions. By raising awareness, promoting preventive strategies, and embracing advancements in research and practice, dental professionals can work collaboratively to combat periodontal diseases and improve the oral and systemic health of individuals throughout the UK.

No comments yet