Storage Area Networks (SANs) are a popular storage networking architecture used by enterprises for business-critical applications that require high throughput and low latency. In this guide, we will explore what SAN storage is, how it works, and its benefits
What is SAN Storage?
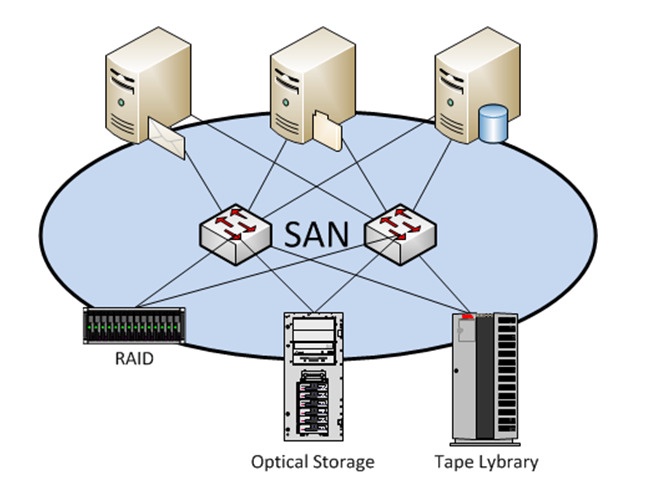
A SAN is a block-based storage architecture that connects servers to their logical disk units (LUNs) . A LUN is a range of blocks provisioned from a pool of shared storage and presented to the server as a logical disk. The server partitions and formats those blocks, typically with a file system, so that it can store data on the LUN just as it would on local disk storage.
How Does SAN Storage Work?
SAN storage separates the storage system from the rest of the local area network (LAN) . This way, it improves application performance, data protection, and disaster recovery if needed. SANs make storage management simpler with centralized features that can be applied to all the storage resources on the SAN. Features can include data encryption, data compression, and data deduplication.
SANs can be made up of thousands of SAN host servers and storage devices that can be scaled out by adding new hosts and storage capacity to meet changing business needs. In a SAN, storage remains independent of applications and is accessible through multiple paths. If a communication failure occurs, the network fabric can use an alternative path to ensure data availability.
Benefits of SAN Storage
High Performance: SAN storage is a high-performance, high-speed network of storage, servers, and devices that allows access to consolidated, block-level storage. Multiple client devices can access it, and it usually appears to the client OS as a disk.
Scalability: SAN storage can be scaled easily to suit evolving business needs. Should you need more storage, more capacity can be added when and as it is required.
Data Protection: Data backup should always be a major consideration, and if using SAN, you only need a single backup server for data that is potentially scattered across multiple locations. A well-designed and distributed SAN can withstand multiple device or component failures, keeping the data safe.
Centralized Management: Storing data in centralized shared storage architecture like SANs allows organizations to manage storage from a collective place and apply consistent policies for security, data protection, and disaster recovery.
SAN vs. NAS
A SAN and network-attached storage (NAS) are two different storage architectures. While SANs are block-based storage, NAS is file-based storage. In a NAS, data is stored in files and accessed over a network using protocols such as NFS or SMB. SANs are typically used for high-performance applications that require low latency and high throughput, while NAS is used for file sharing and storage consolidation.
In conclusion, SAN storage is a high-performance, scalable, and centralized storage architecture that provides block-level storage to multiple client devices. It is ideal for business-critical applications that require low latency and high throughput. SANs are designed to remove single points of failure, making them highly available and resilient.

No comments yet