Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a severe condition in which there is a sudden blockage in the blood flow to the heart. It includes heart attacks and unstable angina. Time is crucial in managing ACS to prevent further damage to the heart muscle. Let's explore the timely interventions and treatment protocols that can make a difference.
Recognizing the Symptoms
ACS symptoms can vary, but common signs encompass
- Chest pain or discomfort,
- Shortness of breath,
- Nausea, and
- Sweating
It is essential to recognize these symptoms and act promptly. If you or someone around you experiences ACS symptoms, don't hesitate to call emergency services immediately. Time is critical; the sooner help arrives, the better the chances of survival.
Treatment Protocols
When patients experience Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS), healthcare providers act swiftly to stabilize their condition and minimize further heart damage. Here is a simplified overview of what patients can expect during treatment:
1. Initial Treatment:
- Patients may receive pain relief medications such as morphine or fentanyl to alleviate discomfort.
- Oxygen therapy may be administered to improve breathing.
- Nitroglycerin may be given to widen blood vessels.
- Aspirin and clopidogrel are the medications prescribed to prevent blood clot formation.
2. High-Risk Patients:
Individuals evaluated at high risk for a heart attack, such as those with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI ACS), would most likely receive intensive therapy, which may include several medications and, in some circumstances, early revascularization procedures to open blocked arteries.
3. Intermediate and Low-Risk Patients:
Patients categorized as intermediate or low-risk will undergo prompt evaluation to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Pharmacological and Surgical Management
1. Medications
Patients may receive medications like
- Aspirin or Ticagrelor, such as Axcer 90mg tablet to prevent blood clotting,
- Nitroglycerin widens blood vessels, and
- Pain relievers to alleviate discomfort.
2. Reperfusion Therapy:
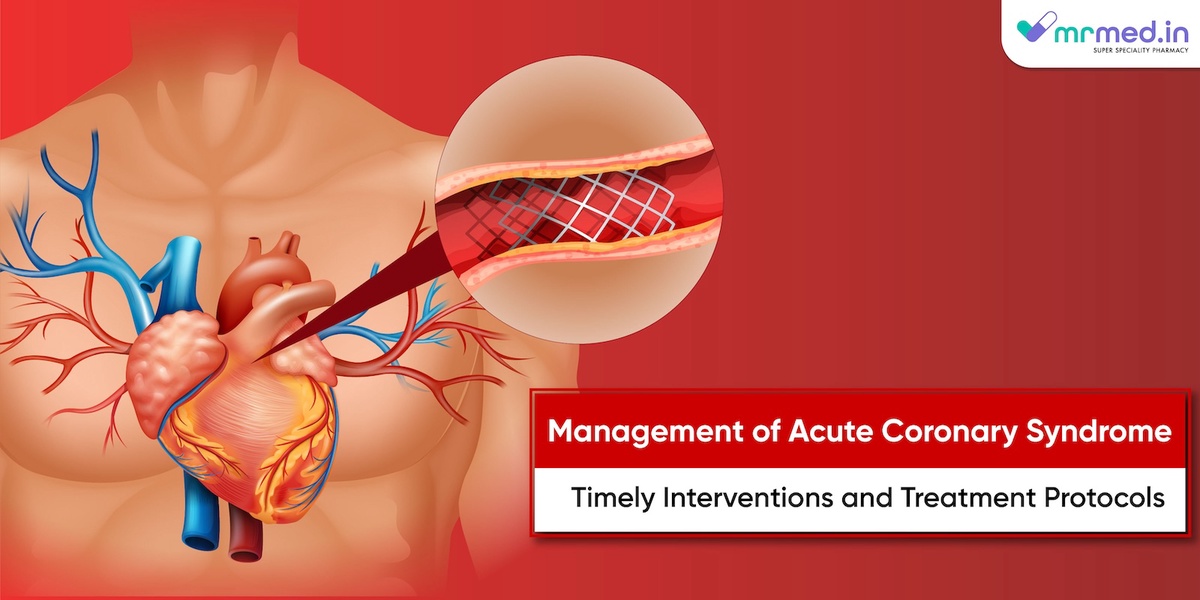
Reperfusion therapy helps to restore blood flow to the heart muscle promptly. It can be achieved through medication (thrombolytics) or invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting.
3. Angioplasty and Stenting:
During the angioplasty procedure, a catheter with a deflated balloon is inserted into the blocked artery. This balloon is then inflated to widen the blocked artery, allowing improved blood flow. A stent, a tiny mesh tube, may be placed to keep the artery open.
4. Rehabilitation
After treatment, cardiac rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery. It involves supervised exercise, education on heart-healthy habits, and emotional support.
5. Management of Post-procedure Complications
Patients are closely monitored for complications, particularly if they have received specific types of stents that may pose a higher risk of complications following the procedure.
6. Preventive Measures
Preventing future ACS episodes involves:
- Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking.
- Eating a balanced diet.
- Exercising regularly.
- Managing stress.
- Taking prescribed medications as directed.
7. Improvements in Treatment Over Time
Adherence to evidence-based guidelines and treatment protocols improves outcomes and enhances survival rates for patients with ACS. Patients must follow their healthcare team's recommendations to promote recovery and long-term heart health.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the potential complications of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
Answer: ACS can lead to several complications, including heart failure, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), cardiogenic shock (when your heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs), and even sudden cardiac arrest (when the heart suddenly stops beating).
2. What is the spectrum of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) clinical presentations?
Answer: ACS can present in various ways, ranging from severe chest pain (a heart attack) to milder symptoms like discomfort or pressure in the chest, shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, or pain that spreads to the arms, neck, jaw, or back.
3. What are the signs and symptoms of acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
Answer: Signs and symptoms of ACS include chest pain or discomfort (which may feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or tightness), shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, sweating, lightheadedness, and pain or discomfort in other areas of the upper body such as the arms, back, neck, or jaw.
4. What is the range of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) physical findings?
Answer: Physical findings in ACS may include abnormal heart sounds, such as murmurs or extra sounds, elevated or irregular heart rate, low blood pressure, signs of heart failure (such as fluid buildup in the lungs or swelling in the legs), and signs of poor blood flow to organs.

No comments yet