Hernias are a common medical condition affecting individuals of all ages. They happen when a tissue or organ pushes through a weak point in the surrounding connective tissue or muscle. While they are generally not life-threatening, hernias can cause discomfort, pain, and complications if left untreated. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and advanced treatment options for hernias, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition and its management.
Types of Hernias
Among the various types of hernias, ventral hernias are a common occurrence. They result from weakened or separated abdominal muscles, allowing abdominal tissues or organs to protrude. Ventral hernias can manifest in different areas of the abdomen, such as the umbilical region (umbilical hernia) or along surgical scars (incisional hernia), and are often characterized by a visible bulge.
Inguinal hernias, on the other hand, are particularly prevalent in men. They occur when a portion of the intestine pushes through the inguinal canal, located in the groin area. These hernias present as a noticeable bulge in the groin or scrotum and can be painful, especially when engaging in activities like heavy lifting or straining during bowel movements.
Hiatal hernias are unique, involving the stomach protruding through an opening in the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the chest from the abdomen. This type of hernia is often associated with conditions like acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), leading to symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing.
Incisional hernias, a subtype of ventral hernias, emerge at the site of previous abdominal surgery incisions. They can develop months or even years after surgery due to weakened scar tissue. Individuals with a history of abdominal procedures should remain vigilant for signs of incisional hernias and seek prompt medical evaluation if any abdominal irregularities arise.
Consult Now: Hernia treatment in Coimbatore
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with hernias is essential for both prevention and early detection. Muscle weakness is a significant contributor to hernia development. Whether due to genetic predisposition, the natural aging process, or chronic straining of the abdominal muscles, weakened muscles create opportunities for organs or tissues to protrude.
Engaging in activities that involve heavy lifting or frequent straining, such as weightlifting or persistent coughing, can elevate the risk of hernias. Pregnancy and childbirth also play a role, as they can exert additional pressure on the abdominal muscles and weaken the abdominal wall.
Age and gender are influential factors, with inguinal hernias being more common in men, while femoral hernias are more frequently observed in women. Chronic medical conditions like obesity, chronic coughing, or chronic constipation contribute to increased abdominal pressure, further heightening hernia risk. Additionally, a family history of hernias may predispose individuals to the condition, with genetics influencing muscle weakness.
Identifying and recognizing these risk factors empower individuals to take preventive measures and seek timely medical attention if they suspect a hernia.
Spotting the Signs: Hernia Symptoms
Early recognition of hernia symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. The signs and symptoms of hernias can vary depending on the type and severity, but often include a visible bulge, localized pain or discomfort, a burning sensation (common in hiatal hernias), difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and, in severe cases, symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
However, it's crucial to acknowledge that not all hernias exhibit noticeable symptoms. Some hernias may remain asymptomatic and be discovered incidentally during routine medical examinations or imaging for other medical concerns. Nonetheless, should any of these symptoms arise, or if a hernia is suspected, seeking prompt medical evaluation is crucial.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
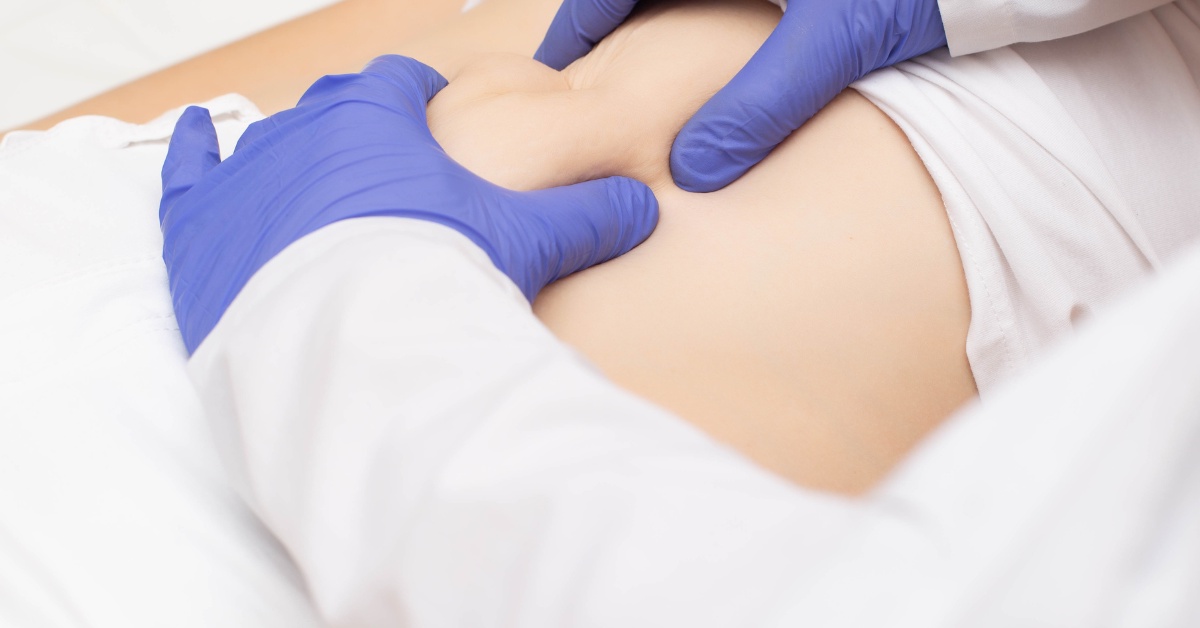
Diagnosing hernias typically involves a combination of reviewing the patient's medical history, performing a physical examination, and employing diagnostic tests. During a physical examination, healthcare providers palpate the affected area to detect signs of a hernia, such as a bulge or tenderness. Patients may be asked to cough or strain during the examination to observe changes in the hernia.
In some cases, medical imaging is necessary to visualize the hernia accurately. Common imaging tests include ultrasound, CT scans, and X-rays, which help determine the hernia's size, location, and severity. In instances where hiatal hernias or internal hernias are suspected, an endoscopy may be conducted. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube equipped with a camera into the esophagus or abdominal cavity to directly visualize the hernia.
Early diagnosis plays a pivotal role in effective hernia management, enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment strategies to the specific type and severity of the hernia.
Treatment Options
Hernia management varies based on factors like hernia type, size, and the presence of symptoms. Options for treatment include both non-surgical and surgical methods.
Non-surgical approaches are often recommended for small, asymptomatic hernias. They may include lifestyle modifications such as weight management, avoiding heavy lifting, and addressing constipation. Supportive garments, such as belts or trusses, can offer temporary relief for certain hernia types. Additionally, medication may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms, such as heartburn or indigestion in hiatal hernias. However, it is important to note that non-surgical methods do not cure hernias but rather help manage symptoms.
Surgical intervention is frequently the primary treatment option for hernias, particularly when they are large, symptomatic, or pose a risk of complications. Surgery aims to repair the weakened muscle or tissue and reposition the protruding organ. Various surgical techniques are employed, including traditional open surgery and minimally invasive procedures like laparoscopic or robotic surgery. The choice of surgical approach depends on the individual's circumstances and the recommendations of their healthcare provider.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following hernia surgery, the recovery process involves effective pain management and adherence to activity restrictions. Patients must diligently follow post-operative instructions to ensure a successful recovery. In some cases, rehabilitation exercises may be recommended to restore strength and reduce the risk of future hernias. It is essential to discuss the recovery plan thoroughly with your healthcare provider and follow it diligently.
Living with Hernias
Long-term hernia management may involve lifestyle adjustments aimed at reducing the risk of recurrence. This can include maintaining a healthy weight, refraining from smoking, and effectively managing chronic conditions that contribute to increased abdominal pressure. Support groups and resources are available to provide guidance and emotional support to individuals living with hernias. While living with a hernia may present ongoing challenges, with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while addressing this common medical concern.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hernias are a prevalent medical condition encompassing various types with diverse causes and treatment options. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, understanding the associated risk factors, and seeking prompt medical evaluation are pivotal steps in effectively managing hernias. Whether through non-surgical approaches or surgical intervention, healthcare professionals can offer guidance tailored to each patient's unique circumstances. Hernias may present challenges, but with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while addressing this common medical concern. Remember, early detection and timely intervention play a crucial role in achieving the best possible outcomes in hernia management. Consult the hernia specialist hospital in Coimbatore to get the best treatment.

No comments yet