There is limited research on the long-term effectiveness of epidural steroid injections (ESI) in older adults despite the high prevalence of back and leg pain in this age group. We tested the hypothesis that older adults undergoing ESI compared with patients not receiving ESI: have worse pain, disability, and quality of life (“outcomes”) before ESI, have improved outcomes after ESI, and have improved outcomes due to a specific effect of ESI.
Methods
We prospectively studied patients aged ≥65 years who presented to primary care with new episodes of back pain in three US health systems (BOLD registry). Outcomes were leg and back pain intensity, disability, and quality of life, assessed at baseline and at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months of follow-up. We categorized participants as: ESI within 6 months of the index visit (n = 295);ESI within 6 months (n = 4809); no ESI within 6 months, propensity-score matched group 1 (n = 483). We analyzed the data using linear regression and Generalized Estimating Equations.
Result
Pain intensity, disability, and quality of life at baseline were significantly worse at baseline in patients with ESI (group 1) than in group 2. Improvements from baseline to 24 months in all outcomes were statistically significant for group 1. However, no statistically significant differences were observed between output trajectories for groups 1 and 3 with matched propensity scores.
Conclusions
Older adults treated with ESIs experience long-term improvement. However, the improvement is unlikely to be the result of a specific ESI effect.
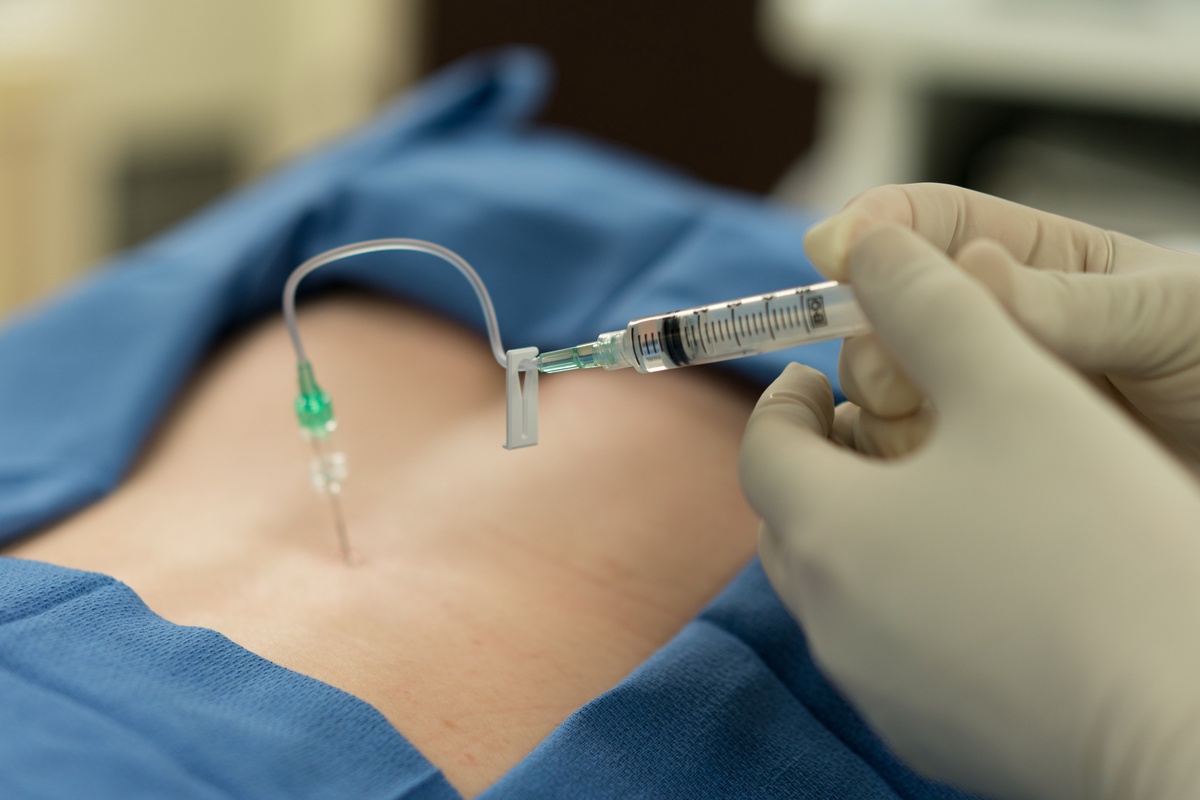
Common Factors that May Affect the Success of the Injection
The effectiveness of an epidural depends on many factors, including:
- Underlying condition: This injection treatment is usually more effective in managing low back pain with radiating leg pain or sciatica than low back pain alone. While the injection can also be used to treat non-radicular, localized back pain in Dallas, the effectiveness can be low.
- Submission route: Research shows that the transforaminal and interlaminar route can obtain more effective results compared to the caudal route.
- Type of steroid:Poorly soluble or particulate steroids such as methylprednisolone or triamcinolone have a long duration of action. Water-soluble or nonparticulate steroids such as dexamethasone are considered safer than particulate steroids, but they tend to be short-lived.
The injection can sometimes be used in combination with a comprehensive rehabilitation program to increase the likelihood of longer-term pain relief and return to daily activities.
Other factors that may affect the outcome of this treatment include the skill and experience of the physician administering the injection, the use of guided fluoroscopy, and the general health of the patient. The treatment may also be more effective in treating acute pain (versus chronic symptoms).
Importance
In this large, two-year, prospective study of older adults with new episode fusion low back pain, back pain, leg pain, disability, and improvement in quality of life after epidural steroid injections; however, propensity score comparisons revealed that the improvement was unlikely due to a specific effect of the injections, suggesting that epidural steroids are unlikely to provide long-term benefits in older adults with new episodes of back and leg pain.

No comments yet