In the dynamic landscape of cancer treatment, the spotlight has shifted towards immunotherapy, a revolutionary approach harnessing the body's immune system to combat cancer. This article explores the various types of immunotherapy and draws a sharp contrast between immunotherapy and chemotherapy, offering insights into their mechanisms, benefits, and limitations.
Types of Immunotherapy
-
Checkpoint Inhibitors:
- Mechanism: Checkpoint inhibitors are drugs that block certain proteins on immune cells, essentially releasing the brakes on the immune system. This allows immune cells to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Applications: These inhibitors are effective against a variety of cancers, including melanoma, lung cancer, and bladder cancer.
-
CAR-T Cell Therapy:
- Mechanism: Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy involves modifying a patient's own T cells to express a receptor that targets cancer cells. Once infused back into the patient, these modified cells seek and destroy cancer cells.
- Applications: CAR-T has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma.
-
Cancer Vaccines:
- Mechanism: Cancer vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Unlike traditional vaccines that prevent infectious diseases, cancer vaccines aim to treat existing cancer.
- Applications: Prostate cancer and certain types of melanoma are among the cancers targeted by therapeutic cancer vaccines.
-
Dendritic Cell Therapy:
- Mechanism: Dendritic cells, crucial for activating the immune response, are extracted from the patient, loaded with cancer antigens, and reintroduced into the body. This primes the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Applications: Dendritic cell therapy is explored in various cancers, including breast cancer and glioblastoma.
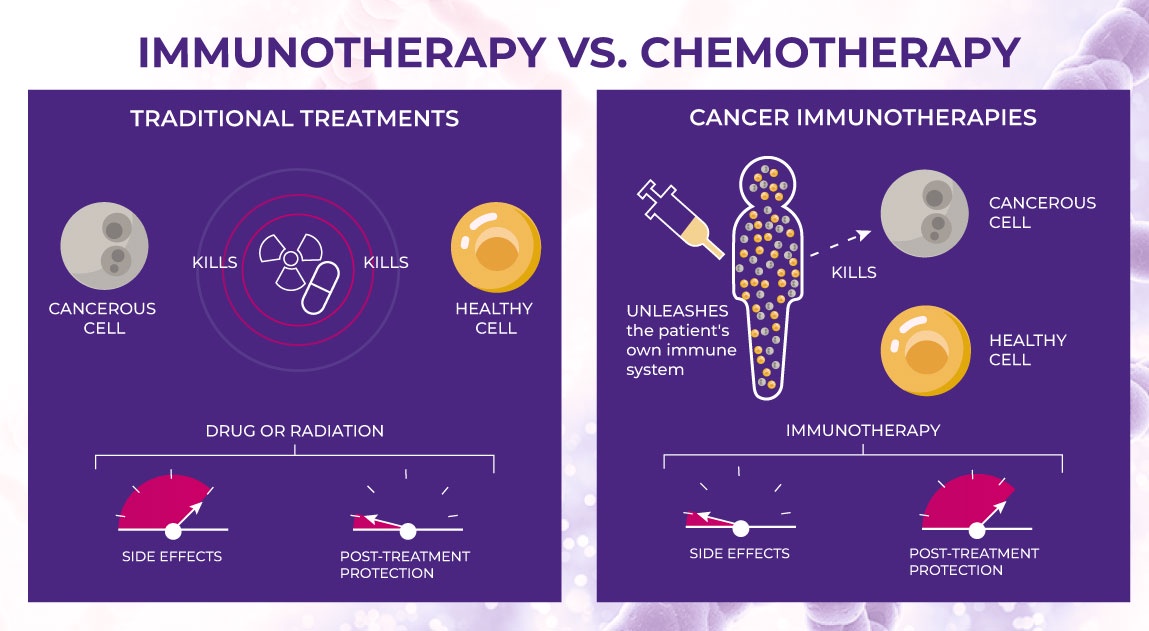
Immunotherapy vs. Chemotherapy
-
Mechanism of Action:
- Immunotherapy: Stimulates the body's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to directly kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
-
Specificity:
- Immunotherapy: Targets specific molecules or cells associated with cancer, offering a more targeted approach.
- Chemotherapy: Non-specifically targets rapidly dividing cells, affecting both cancer and healthy cells.
-
Side Effects:
- Immunotherapy: Generally causes fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy. Common side effects include fatigue, rash, and flu-like symptoms.
- Chemotherapy: Associated with more severe side effects, including nausea, hair loss, and suppression of the bone marrow.
-
Treatment Duration:
- Immunotherapy: Treatment may continue for an extended period, allowing the immune system to sustain its attack on cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Typically administered in cycles with breaks to allow the body to recover from the impact on healthy cells.
-
Efficacy:
- Immunotherapy: Has shown remarkable efficacy in certain cancers, especially those with specific genetic markers.
- Chemotherapy: Effective in rapidly dividing cancers but may lead to resistance and have limitations in certain cancer types.
The Evolving Landscape
Immunotherapy represents a paradigm shift in cancer treatment, offering a more nuanced and targeted approach compared to the blunt force of chemotherapy. The field continues to evolve, with ongoing research exploring combination therapies, identifying biomarkers for treatment response, and addressing challenges such as resistance.
In Conclusion
As we traverse the realms of cancer treatment, the emergence of immunotherapy marks a pivotal moment. The diverse types of immunotherapy, each with its unique mechanisms and applications, exemplify the dynamic nature of precision medicine. Contrasting immunotherapy with chemotherapy reveals a landscape where personalized and targeted approaches redefine the possibilities in the fight against cancer.
While both immunotherapy and chemotherapy play crucial roles in cancer care, the former represents a stride towards treatments that not only combat cancer effectively but also prioritize the well-being of the patient. As research and innovation propel us forward, the synergy between different modalities promises a future where the complexities of cancer are met with tailored, effective, and compassionate solutions.

No comments yet