An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied or grid-connected solar system, is a photovoltaic system directly connected to the electrical grid. In this setup, solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, which is converted from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) by inverters. Unlike off-grid systems, which require batteries for energy storage, on-grid solar systems do not store excess electricity locally but instead feed it directly into the utility grid. This allows homeowners, businesses, and institutions to offset their electricity consumption with clean and renewable solar energy while remaining connected to the grid for additional power when needed. Through net metering arrangements, the utility company can credit or compensate for excess electricity produced by the solar system, providing financial incentives for solar adoption and promoting sustainable energy practices. On-grid solar systems are a popular choice in urban areas and regions with reliable grid infrastructure, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution to meeting energy needs.
How Does On Grid Solar System Work
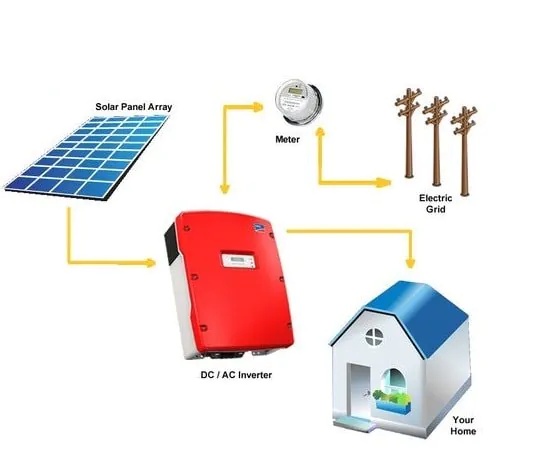
An on-grid solar system works by harnessing sunlight through solar panels and converting it into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
Solar Panels: Photovoltaic (PV) panels, typically installed on the roof or in an open area with maximum exposure to sunlight, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Inverter Conversion: The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC is the standard form of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
Grid Connection: The AC electricity generated by the solar panels is then fed into the electrical grid through a bi-directional meter (commonly known as a net meter). This meter measures both the electricity consumed from the grid and any excess electricity generated by the on-grid solar system in India.
Electricity Consumption: When the solar panels produce more electricity than is needed on-site (e.g., during sunny periods when energy demand is low), the excess electricity is exported to the grid. Conversely, when energy demand exceeds the electricity generated by the solar panels (e.g., at night or during cloudy weather), electricity is drawn from the grid.
Net Metering: Through net metering arrangements, the utility company keeps track of the difference between the electricity consumed from the grid and the electricity exported to the grid by the solar system. Consumers are typically credited or compensated for any excess electricity generated, which can offset their electricity bills.
Grid Backup: In on-grid solar systems, the electrical grid serves as a backup source of power when solar energy production is insufficient to meet demand. This ensures a reliable and uninterrupted power supply, even during periods of low sunlight or high energy consumption.
Benefits of grid-connected solar system
Grid-connected solar systems offer several benefits:
Reduced Electricity Bills: By generating your electricity from solar panels, you can significantly reduce your reliance on grid power, leading to lower electricity bills over time. Excess electricity generated by the solar system can be exported to the grid, offsetting your electricity costs through net metering arrangements.
Financial Incentives and Savings: Many governments and utility companies offer financial incentives, such as rebates, tax credits, and feed-in tariffs, to encourage the installation of grid-connected solar systems. These incentives can help offset the upfront costs of installation and accelerate the return on investment.
Environmental Impact: Grid-connected solar systems produce clean and renewable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to solar energy, you can contribute to mitigating climate change and improving air quality, leading to a more sustainable future.
Energy Independence: Grid-connected solar systems provide a degree of energy independence by generating electricity on-site. This reduces dependence on centralized power plants and enhances resilience against power outages or disruptions in the grid.
Low Maintenance: Solar panels have minimal maintenance requirements and typically have long warranties. Once installed, grid-connected solar systems require little ongoing maintenance, providing a reliable source of electricity with minimal hassle.
Increased Property Value: Homes and businesses with grid-connected solar systems often have higher property values and may be more attractive to potential buyers. Solar panels are considered a valuable asset that can enhance the appeal and marketability of a property.
Scalability and Flexibility: Grid-connected solar systems can be easily scaled up or expanded to accommodate changing energy needs. Additional solar panels can be added to the system as energy demand increases, providing flexibility and adaptability over time.
Promotion of Renewable Energy: By installing a grid-connected solar system, you are contributing to the growth of renewable energy infrastructure and helping to diversify the energy mix. This supports the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy system for the future.
Components of on-grid solar system
An on-grid solar system comprises several key components working together to harness solar energy and feed it into the electrical grid. Here are the main components:
Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules): Solar panels are the primary component of a solar system. They contain photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
Inverter: The inverter is a crucial component that converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used in most homes and businesses and is compatible with the electrical grid.
Mounting Structure: Solar panels need to be mounted securely in place, typically on rooftops or ground-mounted structures, to maximize exposure to sunlight. Mounting structures provide support and ensure the optimal angle and orientation of the solar panels for maximum energy production.
DC Disconnect: A DC disconnect switch is installed between the solar panels and the inverter to allow for safe maintenance and emergency shutdown of the DC electrical circuit.
AC Disconnect: An AC disconnect switch is installed between the inverter and the electrical panel of the building to allow for safe maintenance and emergency shutdown of the AC electrical circuit.
Bi-directional Meter (Net Meter): The bi-directional meter measures the electricity consumed from the grid and any excess electricity generated by the solar system exported to the grid. It enables net metering, allowing homeowners or businesses to receive credits or compensation for the excess electricity they produce.
Electrical Panel (Breaker Panel): The electrical panel serves as the distribution point for electricity within the building. The AC electricity produced by the solar system is connected to the electrical panel, where it can be used to power electrical appliances and devices.
Grid Connection: The solar system is connected to the electrical grid through the building’s electrical panel. This allows for seamless integration of solar-generated electricity with grid power, ensuring a reliable and uninterrupted power supply.
Grounding Equipment: Grounding equipment, including ground rods and grounding wires, is installed to ensure the safety of the solar system by providing a path for electrical faults to dissipate into the ground safely.
on grid solar system price in India
As of my last update in January 2022, the price of on-grid solar systems in India typically ranged from around ₹40,000 to ₹60,000 per kilowatt (kW) of installed capacity for residential installations. This means that the total cost of installing a typical 5 kW residential solar system could range from ₹2,00,000 to ₹3,00,000.
However, please note that these on-grid solar system prices are approximate and can vary based on various factors such as:
System Size: Larger solar systems typically have a lower per kW cost compared to smaller systems due to economies of scale.
Component Quality: The price can vary depending on the quality and brand of solar panels, inverters, mounting structures, and other components used in the system.
Installation Complexity: Factors such as roof type, shading, and site-specific challenges can affect installation costs.
Labor and Installation Fees: Labor costs can vary depending on local labor rates, installation time, and any additional work required.
Government Subsidies and Incentives: Subsidies, incentives, and tax credits provided by the government can help offset the upfront cost of installing a solar system, making it more affordable for consumers.
Additional Costs: Other factors such as permits, approvals, grid connection fees, and any necessary upgrades to the electrical system may also contribute to the total cost.
Conclusion - on-grid solar systems represent a pivotal step toward a sustainable energy future, offering a myriad of benefits to individuals, businesses, and communities. By seamlessly integrating solar energy production with the existing electrical grid, these systems provide a reliable and cost-effective means of harnessing clean and renewable energy. The economic savings, environmental benefits, and energy independence afforded by on-grid solar systems make them an attractive choice for consumers looking to reduce their carbon footprint while lowering electricity costs. Moreover, on-grid solar systems play a crucial role in advancing the transition toward a more resilient and decentralized energy infrastructure, promoting energy security, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. As technology continues to evolve and costs decline, the widespread adoption of on-grid solar systems is poised to accelerate, driving a sustainable energy revolution that benefits both present and future generations.

No comments yet